What is a Liquid 3D Printer and How Does It Work?
The rise of the liquid 3D printer marks a significant milestone in additive manufacturing. According to a recent report by Industry Research, the liquid 3D printing market is projected to grow exponentially, reaching an estimated value of $5 billion by 2025. This growth is driven by industries such as automotive, aerospace, and healthcare. Experts like Dr. Emily Carter, a leading figure in 3D printing technology at Advanced Materials Institute, states, "Liquid 3D printing expands the boundaries of traditional manufacturing."
Liquid 3D printers utilize photopolymerization to create detailed structures layer by layer. This technology allows for rapid prototyping and complex designs that were once deemed impossible. While the advantages are clear, there are challenges to address. The materials used can sometimes present issues with consistency and performance, leading to potential product failures. Despite progress, this field is still evolving and requires ongoing innovation to meet industry demands.
As with any technological advancement, the liquid 3D printer also has its drawbacks. The complexity of post-processing steps can complicate workflows, and the need for precise calibration is paramount. Industry stakeholders must prioritize further research and development. Addressing these challenges will be crucial for harnessing the full potential of liquid 3D printing.
Table of Contents
[Hide]
What is a Liquid 3D Printer?
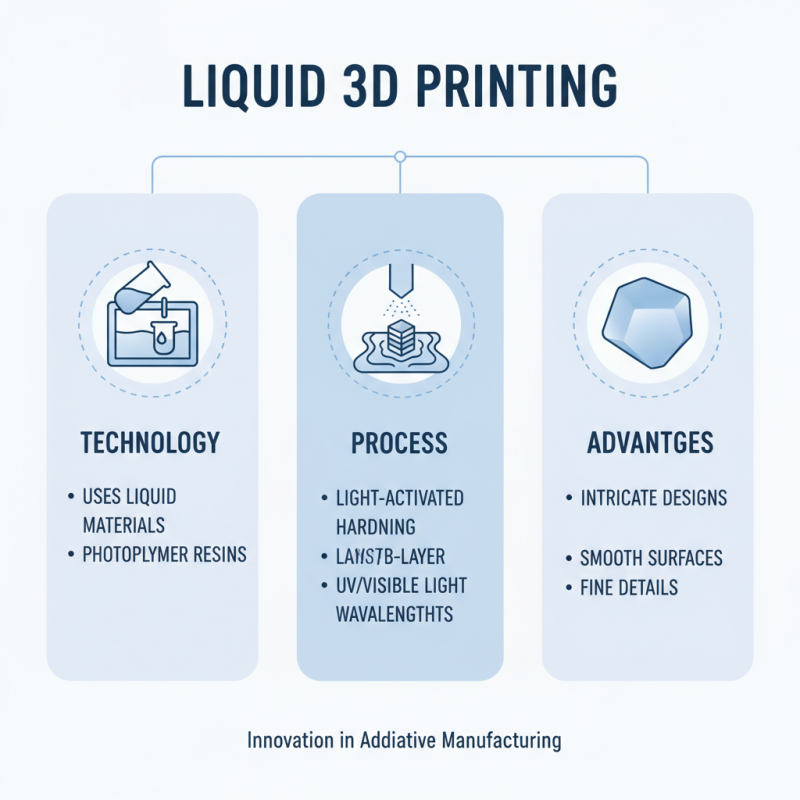
Liquid 3D printers are an innovative technology that uses liquid materials to create three-dimensional objects. Unlike traditional printers that use filament or powder, these printers employ photopolymer resins. When exposed to specific light wavelengths, the liquid hardens, building the model layer by layer. This method allows for intricate designs, producing smooth surfaces and fine details.
Working with liquid materials can be tricky. It's essential to have the right environment to avoid contamination. Dust and dirt can compromise the printing process. Regular cleaning of the printer is crucial.
Tip: Always wear gloves when handling resins. It prevents skin irritation and maintains cleanliness.
The resin must also be stored properly. Light can cause it to harden prematurely. Use opaque containers to protect the material. Remember to follow safety guidelines when mixing resins. This can sometimes result in uneven textures. A little care can go a long way in achieving a successful print.
Tip: Test prints can help assess the quality before committing to final designs. This practice helps identify potential issues early.
Key Components of Liquid 3D Printing Technology
Liquid 3D printing technologies have gained traction recently, primarily due to their unique components and processes. These printers use a resin-based method, which allows for precise layering of materials. The most critical component is the light source. Typically, ultraviolet (UV) light hardens the liquid resin. This process enables designers to create intricate details and smooth surfaces more efficiently.
Another essential element is the build platform. It acts as the foundation for the object being printed. The platform needs to be leveled accurately to ensure a successful print. An uneven surface can lead to failures, wasting valuable time and resources. Studies indicate that nearly 30% of printing errors stem from improper calibration of the build platform. These mistakes highlight the necessity of continuous monitoring and adjustment throughout the printing process.
The resin itself also significantly impacts the final product's quality. Different formulations can exhibit varied properties, such as tensile strength and flexibility. Recent reports found that more than 40% of users seek materials that combine durability with ease of use. Despite technological advancements, challenges remain. The environmental impact of disposing of resin waste demands attention, as does the learning curve associated with mastering these complex printers.
What is a Liquid 3D Printer and How Does It Work? - Key Components of Liquid 3D Printing Technology
| Component | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Liquid Resin | A photopolymetric material that hardens upon exposure to light. | Acts as the primary building material for printing. |
| Build Platform | A flat surface where the printed object is formed. | Supports the structure being printed layer by layer. |
| Light Source | Typically a UV light or laser used to cure the resin. | Initiates the polymerization process of the liquid resin. |
| Control System | An electronic setup that regulates printing parameters. | Ensures the precise movement and curing of resin. |
| Resin Tank | Holds the liquid resin during the printing process. | Provides a reservoir from which the resin is drawn. |
| Z-Axis Mechanism | Moves the build platform vertically for layer-by-layer printing. | Allows for accurate layering by adjusting the height. |
How Liquid 3D Printing Differs from Traditional Methods
Liquid 3D printing represents a revolutionary approach in the world of additive manufacturing. This method utilizes a liquid material that is cured to create objects layer by layer. Unlike traditional 3D printing, which often uses solid filaments, liquid printing offers greater versatility in material selection. The transition to a liquid phase allows for intricate designs that are hard to achieve with conventional methods.
In traditional 3D printing, the process can be slow and often involves cumbersome setups. Liquid 3D printing, on the other hand, can produce components faster. The curing process can be controlled precisely, allowing for quick adjustments and detailed results. However, this technology is still evolving. Challenges remain in achieving uniformity and preventing imperfections in the final products. There are risks of bubbles and defects that might affect structural integrity. As this method advances, refining these aspects will be crucial for wider adoption.
The Printing Process: Step-by-Step Guide
Liquid 3D printers use a fascinating printing process. They rely on liquid resin as the primary material. The printer starts with a build platform submerged in a vat of resin. Layer by layer, the object is formed as the resin hardens. This process is called photopolymerization. Light sources cure the resin, solidifying it into precise shapes.
After the initial layer, the platform rises slightly. This allows fresh resin to flow over the previously hardened layer. Each layer adds complexity and detail to the final product. Begin with a 3D model, designed for printing. Ensure that the design is optimized for resin flow. Sometimes, supports are needed to keep overhanging parts intact. Miscalculations can lead to failures, and getting the right support structure is tricky.
After printing, the object needs post-processing. Excess resin must be cleaned off carefully. A wash in isopropyl alcohol is often used. Curing under UV light enhances the strength of the print. However, this step can be uneven if not done correctly. The result? A strong, detailed 3D object, sometimes with imperfections. Learning from these imperfections is part of the journey in mastering liquid 3D printing.
Applications and Future of Liquid 3D Printing
Liquid 3D printing offers unique potential across various industries. This technology uses a liquid resin that hardens when exposed to light. As it develops, it can create intricate and complex designs. The precision of liquid printing allows for highly detailed products, which is invaluable in fields like medical and aerospace engineering.
[Image]
In the medical sector, custom prosthetics and implants are on the rise. They allow for personalized solutions to meet specific patient needs. However, challenges remain in achieving regulatory approvals. The aerospace industry shows great interest as well, where lightweight parts can greatly enhance fuel efficiency. Yet, the material costs remain high, limiting broader implementation.
Future applications of liquid 3D printing may include consumer products and architecture. Imagine fully customizable furniture or even houses tailored to individual preferences. However, the technology must overcome barriers in speed and scalability. The dream of mass production might still be a distant goal. Innovations are unfolding, yet the journey involves significant trial and error. Exploring these advancements is both exciting and uncertain.
Related Posts
-

Unlocking the Future of Creativity with 3D Printers for Every Home
-
What is an 8K 3D Printer? Exploring Benefits and Applications in 2023
-

The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Best Desktop SLS Printer for Your 3D Printing Needs
-

Challenges Faced by Businesses in Adopting Commercial 3D Printers
-
Unlocking the Future Best 8K 3D Printer for Global Buyers
-

Revolutionizing Oral Care: The Impact of Dental 3D Printers on Modern Dentistry