What is a plastic printer and how does it work?
A plastic printer is an innovative device transforming how we create objects. It utilizes melted plastic filaments to build items layer by layer. This technology captures imagination and sparks curiosity among hobbyists and engineers alike.
Understanding how a plastic printer operates reveals its complexity. The printer heats plastic until it flows, then deposits it precisely according to digital designs. For many users, mastering this intricate process can be both rewarding and challenging. Calibration issues may arise, and knowledge of materials is essential. This can lead to both excitement and frustration.
Plastic printers enable unique creations, yet they are not without limitations. Quality can vary based on the printer and conditions. Users often find themselves reflecting on their approaches and outcomes. Each print offers lessons, whether success or failure. This journey is part of the allure, pushing boundaries of creativity and innovation.
Table of Contents
[Hide]
What is a Plastic Printer?
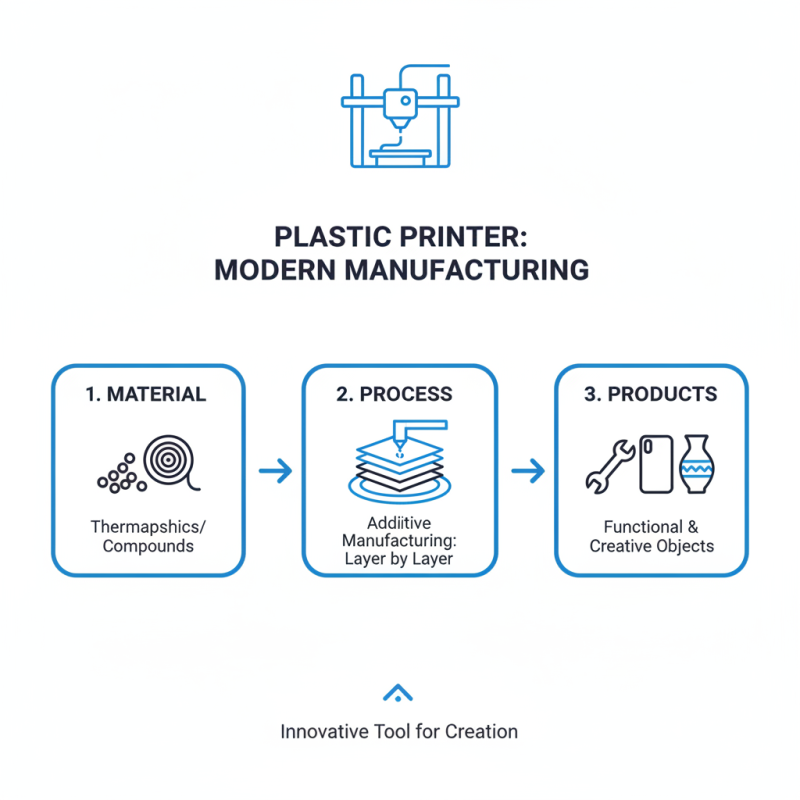
A plastic printer is a groundbreaking tool in modern manufacturing. It transforms plastic materials into functional and creative objects. Leveraging advanced technology, this printer operates through a process known as additive manufacturing. In simple terms, it builds items layer by layer, utilizing thermoplastics or other plastic compounds.
The global 3D printing market has seen dramatic growth. As per recent industry reports, it is projected to reach $34.8 billion by 2024. This expansion highlights the increasing interest in plastic printing across various sectors like aerospace and healthcare. In 2020, approximately 80% of manufacturers adopted additive manufacturing technologies, emphasizing its significance.
Tips: Always keep the printer’s nozzle clean. A clogged nozzle can impact print quality. Regular maintenance ensures consistent output.
Additionally, understanding the types of plastics available is essential. Different plastics have varied properties. For instance, PLA is biodegradable but may not withstand high temperatures. PETG offers durability and flexibility but can be challenging for beginners. Choosing the right material is crucial for achieving desired results. Remember, experimentation is vital in this learning process. Not every print will succeed. Reflecting on failures can lead to growth in skills and creativity.
Types of Plastic Printers and Their Applications
Plastic printers are versatile tools used in various industries. They create objects by melting plastic and depositing it layer by layer. There are different types of plastic printers, each with unique applications.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) printers are popular for prototyping. They are user-friendly and suitable for home use. However, they may struggle with intricate designs. Stereolithography (SLA) printers offer high detail but can be costly. They are great for jewelry and dental applications. Choosing the right type depends on your project needs.
Tips: Consider the material you want to use. Some plastics are easier to print than others. Also, think about the size of your project. Larger prints might need more attention to detail. Always test your designs with smaller prints first. This can save you time and materials.
The Printing Process: How Plastic Printers Work
Plastic printers use a fascinating process to create three-dimensional objects. They primarily rely on additive manufacturing techniques. Layers of thermoplastic materials are extruded. The printer's nozzle carefully deposits these materials, layer by layer, until the final shape emerges. Each layer cools and solidifies, bonding with the previous one. This method allows for intricate designs that traditional manufacturing techniques often struggle to achieve.
During the printing process, a design file is crucial. It guides the machine on how to construct the object. Precision is key here. Any error in the digital model can result in flaws. Sometimes, the printer may fail to melt the plastic uniformly, leading to weak spots. Users must monitor and adjust settings for temperature and speed. Regular maintenance is essential to prevent clogs and ensure quality output.
Flexibility is one of the greatest advantages of plastic printers. They can work with various materials, from ABS to PLA. However, not all plastics are created equal. Each type has unique properties, affecting strength and flexibility. Users must choose wisely, depending on the project. Experimenting with different plastics can yield unexpected results, often requiring learning from mistakes.
Plastic Printer Usage by Type
This chart represents the distribution of different types of plastic printers used in various applications. The data reflects the growing adoption of 3D printing technology in the manufacturing sector.
Materials Used in Plastic Printing
In plastic printing, various materials play a crucial role in shaping the final product. Commonly used materials include thermoplastics, resins, and filaments. Thermoplastics like PLA and ABS offer versatility in applications. They melt and solidify easily, allowing intricate designs to form. For example, PLA is often chosen for its biodegradable properties. Yet, it can be sensitive to heat, leading to potential warping.
Another significant material is PETG, which combines the best features of both PLA and ABS. It boasts strength and flexibility. This material is also more impact-resistant than PLA, making it suitable for functional parts. On the downside, PETG can be challenging to print with due to its tendency to string during the process.
Resins are also essential in plastic printing, particularly for high-detail applications. They provide a smooth finish and are used in stereolithography. However, the curing process requires precision. If not done correctly, the final product may have defects. Each material choice can significantly impact the outcome. It’s important to consider each option's properties closely.
Benefits and Limitations of Plastic Printing Technology
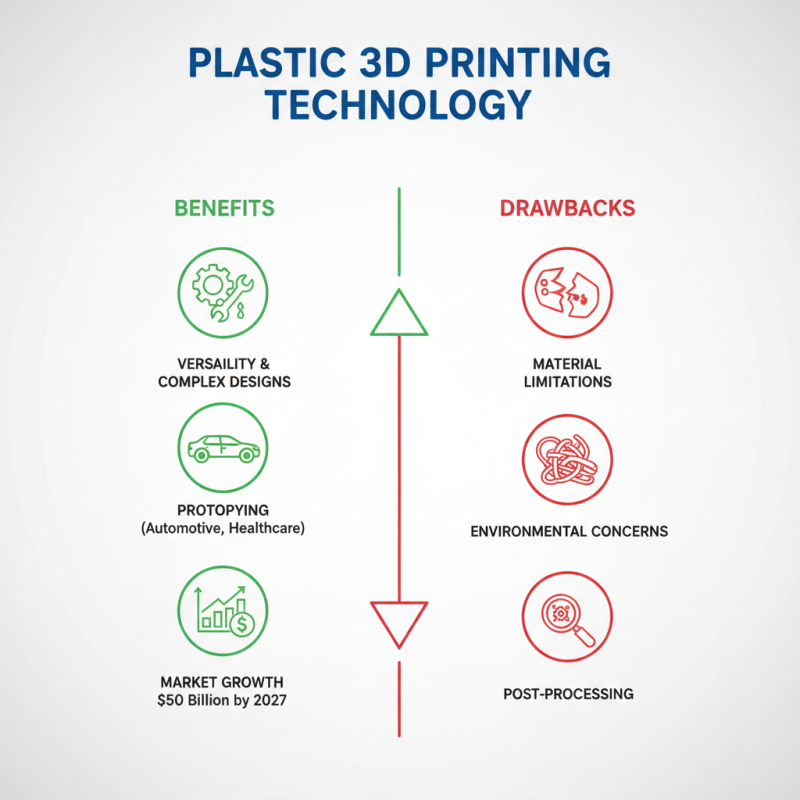
Plastic printing technology offers numerous benefits, but it also has its drawbacks. One major advantage is its versatility. This technology can produce intricate designs and prototypes, suitable for various industries like automotive and healthcare. According to a report by Smithers Pira, the global market for 3D printing in plastic is expected to reach $50 billion by 2027. This growth indicates a strong demand for plastic printing solutions.
However, limitations exist. The quality of printed objects can vary. Factors such as material quality and printer calibration play a significant role. Inconsistencies in layer adhesion can lead to weak points in the final product. Additionally, certain plastics may not be suitable for high-temperature applications. A recent study highlighted that 30% of users reported issues with long-term durability of printed components.
Environmental concerns are another critical aspect. Many plastic materials used in printing are non-biodegradable. As the industry grows, waste management becomes a pressing issue. Companies must reflect on sustainable practices. Balancing innovation with environmental responsibility remains a challenge for many in the field.
Related Posts
-

Unlocking the Future of Creativity with 3D Printers for Every Home
-

What is the Future of 3D Printing Machines in Global Manufacturing
-

Why Laser Sintering 3D Printers Are Revolutionizing Manufacturing Efficiency by 30%?
-

Top 5 Laser Sintering 3D Printers You Need to Know for High Quality Prototyping
-

Top 5 SLS Printers for Exceptional 3D Printing in 2023: Buyers' Guide
-

Best 10 Polymer 3D Printers for Precision and Performance in 2023